NaBEF (China)
The NaBEF (Nutrient addition and Biodiversity Ecosystem Function) experiment was established in January 2019, representing the tropical-subtropical forest ecotone in southern China. The main goals of NaBEF are (1) to examine the species diversity effect on a variety of ecosystem functions and (2) explore how nitrogen and phosphorus addition might affect the relationships between biodiversity and ecosystem functioning.
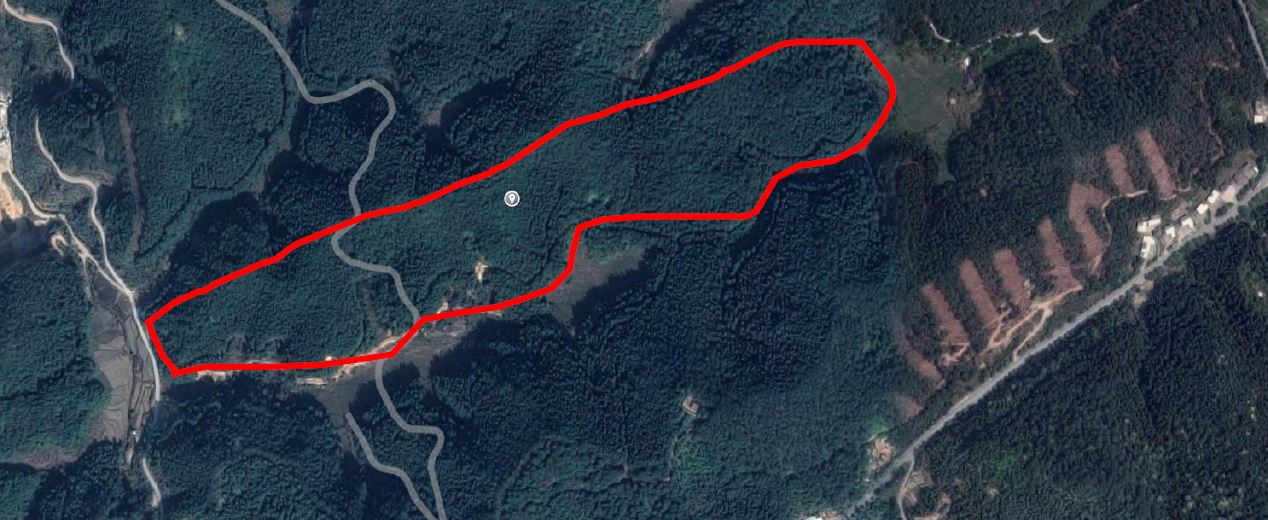
|

|
| Location of the NaBEF site and aerial view of NaBEF from 600 m above (July 2022) |
Design
The NaBEF contains thirty-two tree species according to their shade and drought tolerance. In
total, 299 plots of 12 × 12 m were arranged in a randomized factorial design, with species richness level
ranging from 1, 4, 8, 16, to 32 species. Nutrient addition treatments include nitrogen addition(+N);
Phosphorus addition(+P); Nitrogen and Phosphorus addition(+NP) with a dose of 50, 50, 50+50 kg ha-1
yr-1, respectively; The nutrient treatments were applied to a gradient of species diversity from 1, 4, 8,
and 16, with each treatment combination randomly replicated. The nutrient treatments were applied
beginning in the spring of 2020. In each plot, 256 trees were planted within at a distance of 0.75 m and
a certain number of seedlings were planted outside the plots. In total, 80,000 trees were planted.
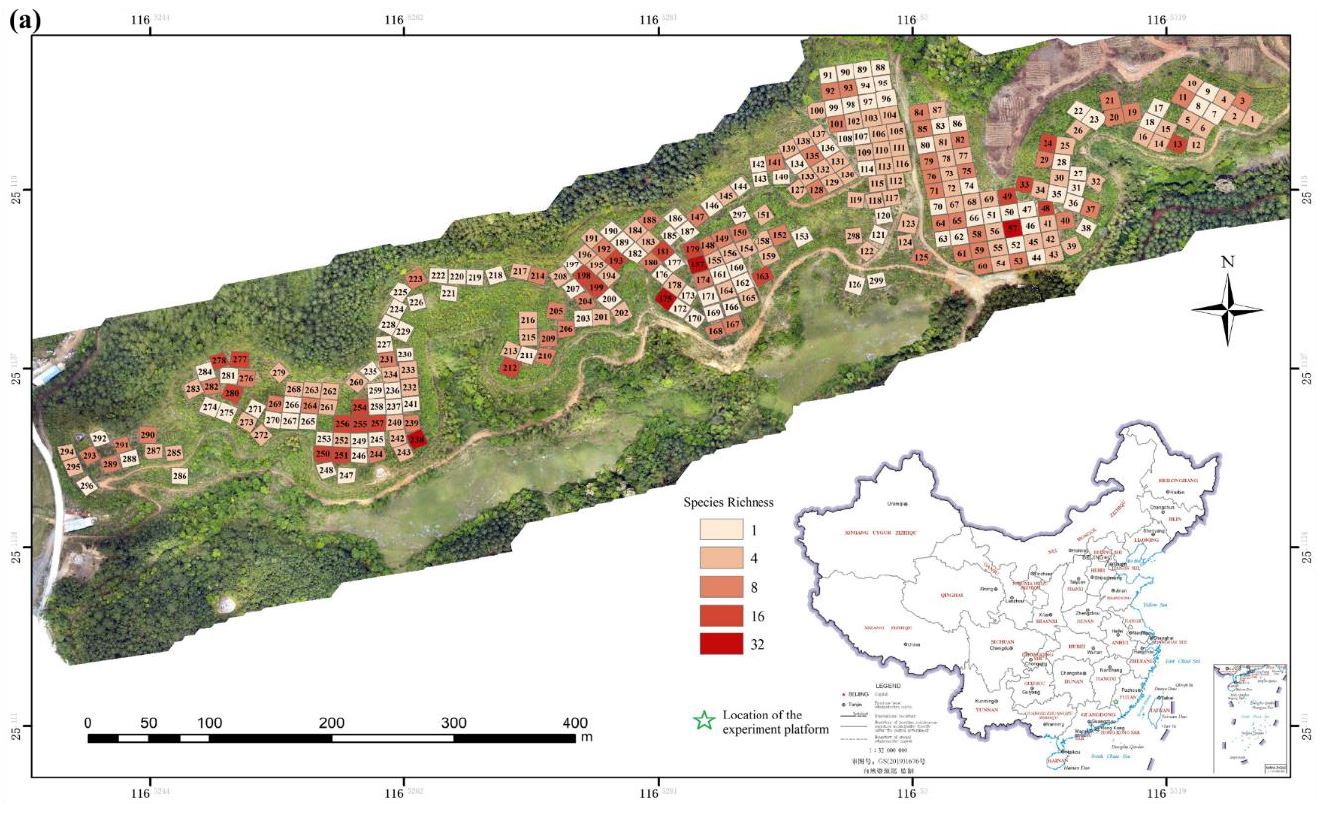 |
| Layout of the NaBEF experiment. |
Site characteristics
| location | Baisha, Shanghang, Longyan, Fuijian (N 25° 06' 52.6" E 116° 31' 48.6") |
|---|---|
| former land use | Cunninghamia lancelotata (Lamb. Hook) plantation |
| altitude | 500 m |
| soil type | Ultisol |
| area | 14 ha |
| no of plots | 299 |
| plot size | 144 m² |
| no of trees planted | 76544 |
| planting date | 2019 |
| diversity variables | species richness, functional diversity (shade and drought tolerance) |
| diversity gradient | 0, 1, 4, 8, 16, 32 sp. |
| size species pool | 32 |
| species pool | Acer palmatum; Alnus trabeculosa; Castanopsis carlesii; Castanopsis fissa; Castanopsis hystrix; Castanopsis sclerophylla; Celtis sinensis; Cinnamomum camphora; Cryptomeria fortune; Cunninghamia lanceolate; Cyclocarya paliurus; Elaeocarpus sylvestris; Euscaphis japonica; Fokienia hodginsii; Hovenia acerba; Lagerstroemia indica; Liquidambar formosana; Lithocarpus glaber; Machilus pauhoi; Manglietia fordiana; Michelia macclurei; Michelia maudiae; Mytilaria laosensis; Ormosia hosiei; Osmanthus fragrans; Phoebe chekiangensis; Phoebe bournei; Pinus massoniana; Quercus variabilis; Sapindus saponaria; Schima superba; Taxus wallichiana |
| tree-to-tree planting distance | 75 cm |
| within plot planting design | triangular design (maximize interspecific competition among traits and species) |
| additional treatments | Nitrogen addition; Phosphorus addition; Nitrogen and Phosphorus addition | additional design info | Nutrient addition covers richness from 1 to 16 |
| contact persons | Zhiqun Huang |
Research
NaBEF studies the effects of species richness on a variety of ecosystem functions such as primary productivity, nutrient and water cycling, litter decomposition, greenhouses gases emissions, soil biota and other trophic groups. Measurements will be repeatedly taken, depending on the subjects investigated.
Extra information
For more information on the NaBEF experiment, send an e-mail to the contact person or explore the publications.
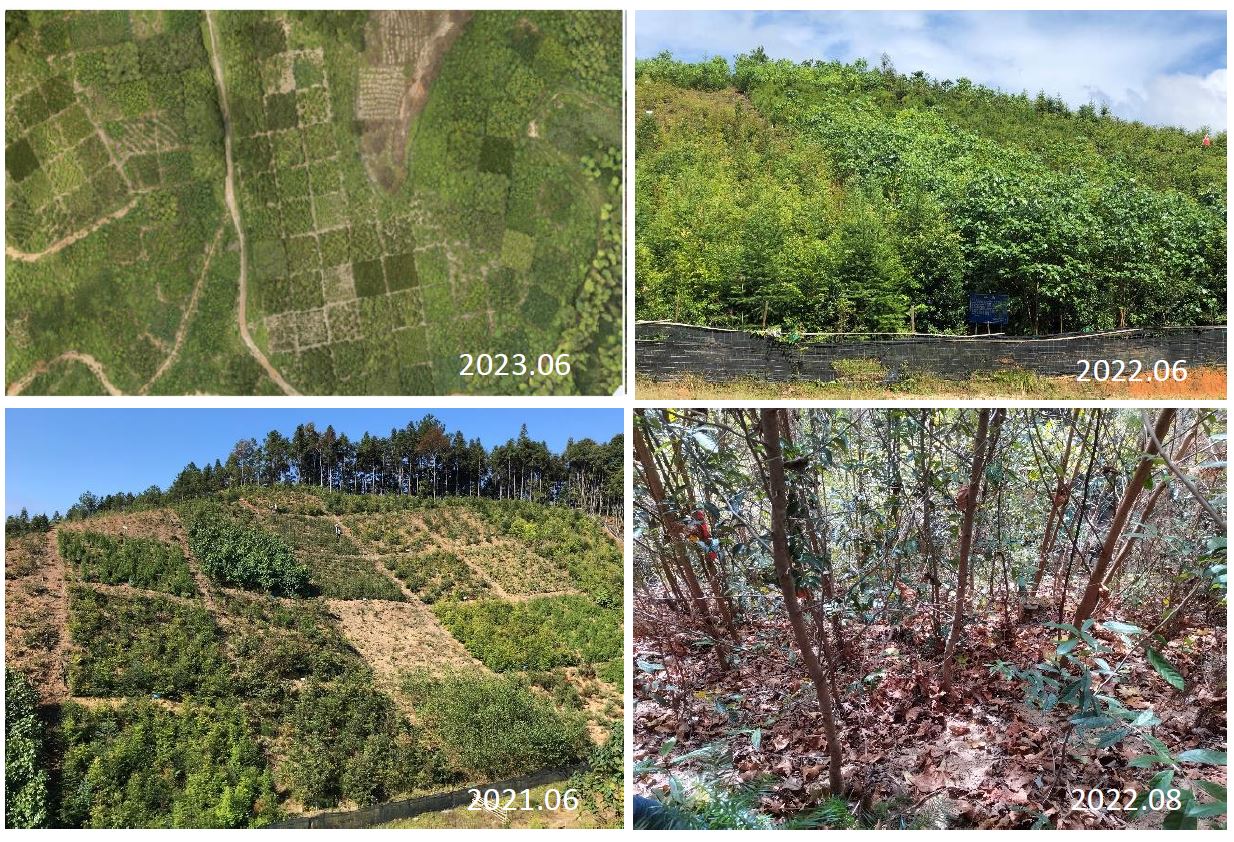

|
| View from the NaBEF site (2021 - 2023) |
